Discharge Instructions: Self-Catheterization for People with a Penis
Your healthcare provider has prescribed self-catheterization for you. This is because you are having trouble urinating naturally. This problem can be caused by injury, disease, infection, or other conditions. Self-catheterization simply means putting a clean, thin, flexible tube (catheter) through the penis and into the bladder to empty urine. This helps you empty your bladder when it won’t empty by itself or empty all the way. You were shown in the hospital how to do self-catheterization. The steps below should help you remember how to do it correctly.
Gather your supplies
You will need:
Get ready
-
Wash your hands and your penis. Use warm soapy water. You can also use a moist towelette. If you are uncircumcised, pull back the foreskin before washing.
-
Lubricate the catheter with the water-soluble lubricating jelly.
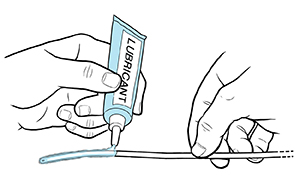 |
| Lubricate catheter. |
Empty your bladder
-
Insert the catheter.
-
Grasp the tip of your penis, holding your penis horizontally from your body.
-
Slowly put the catheter into your urethra. Move it in about 6 to 8 inches or until urine begins to flow. If it doesn’t go in, do this: Take a deep breath and bear down as if you're trying to urinate.
-
If you feel a sharp pain, remove the catheter. Then try again.
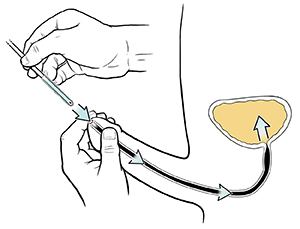 |
| Insert catheter. |
-
Empty your bladder.
-
When the urine starts to flow, advance the catheter tip one more inch.
-
Slightly lower your penis.
-
When the urine stops flowing, slowly remove the catheter.
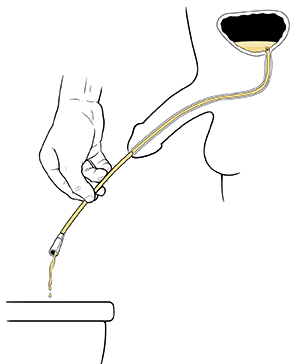 |
| Empty urine. |
Catheter care
If you use a disposable catheter, use a new one each time you empty your bladder. Throw the catheter away when you’re done. If your catheters are reusable, do the following after each use:
-
Wash your hands with soap and warm water.
-
Clean the catheter with soap and warm water.
-
Rinse the catheter, making sure there is no soap left inside or on it.
-
Let the catheter air-dry before storing.
-
Store the catheter in a clean, dry container, such as a plastic bag that seals at the top.
-
Throw away a catheter if the plastic looks cloudy. Follow your healthcare providers instructions on when the catheter should be changed.
-
Wash your hands again. If you used a basin, wash it out.
Follow-up care
Make a follow-up appointment, or as directed.
When to call your healthcare provider
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following:
-
You cannot move the catheter farther in because of resistance
-
Continued feeling of bladder pressure even after inserting the catheter
-
Fever above 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, or as directed by your provider
-
Chills
-
Burning in the urinary tract, penis, or pubic area
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Aching in your lower back
-
Cloudy,or foul smelling urine
-
Specks (sediment) or mucus in the urine
-
Bloody (pink or red) urine
© 2000-2024 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.